Comparison of ASTM A790 and ASTM A928 Standards for Duplex Stainless Steel Pipes
ASTM A790 and ASTM A928 Standards for Duplex Stainless Steel Pipes
Standard Specification
Both standards specify requirements for austenitic-ferritic duplex stainless steel in corrosive environments. ASTM A790 specifies manufacturing requirements for seamless and welded pipes, while ASTM A928 covers only electric-fusion-welded pipes. ASTM A790 requires welding of duplex and super duplex steel pipes without any filler metal, while ASTM A928 allows the use of filler metal for welding.
.
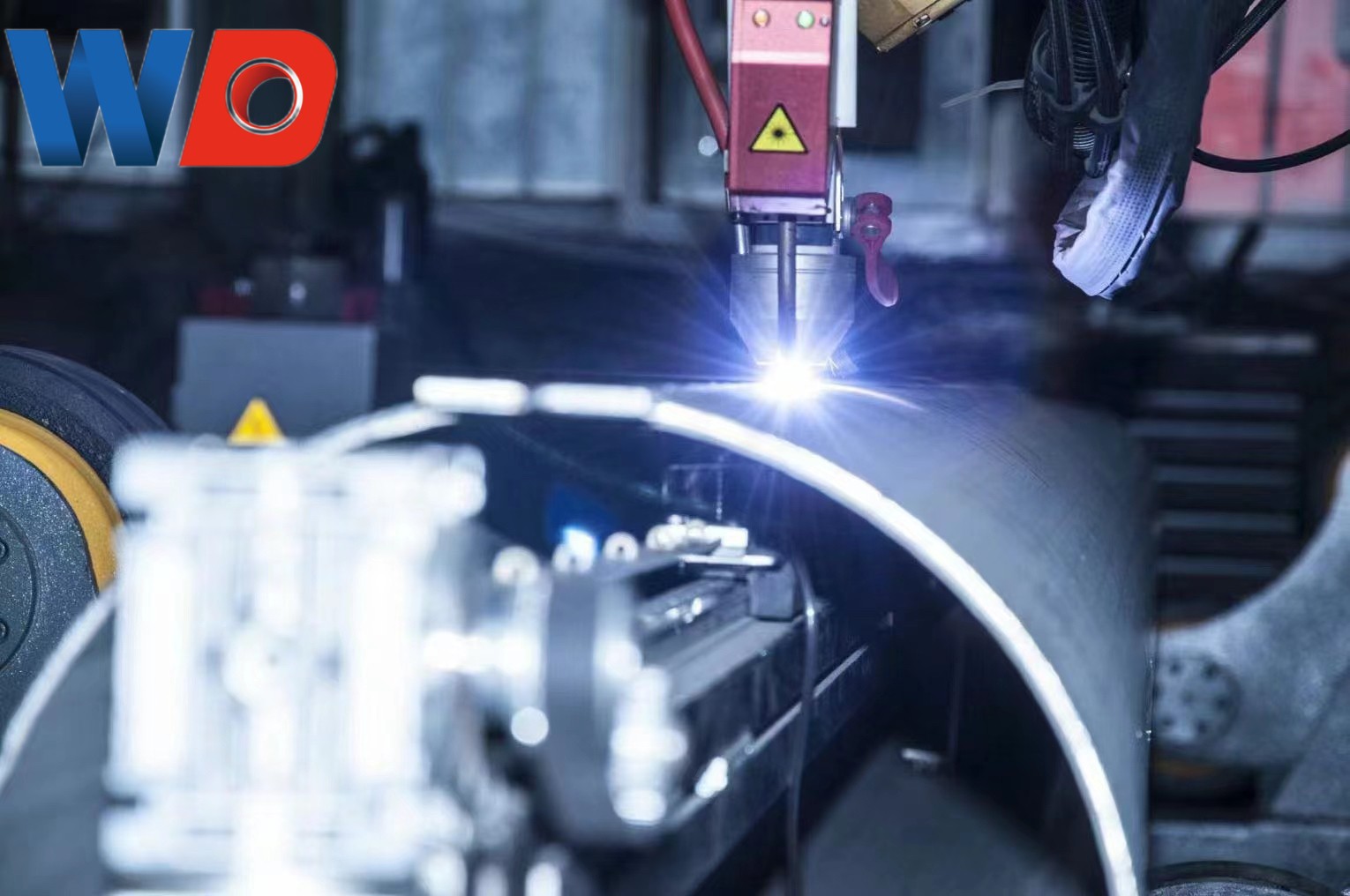

Manufacturing Process
Both standards provide some flexibility in manufacturing processes for producers. For example, if the raw material (coil or plate) has been solution annealed under specific conditions, both standards allow the finished pipe to not be annealed, and this pipe will be marked with the HT-0 symbol. However, ASTM A790 imposes some restrictions on this practice when producing pipes using UNS 31803, S32205, S32750, S32760, and S32520 materials, which require additional corrosion testing. The purchaser and producer must agree on these differences between the two standards.
.

ASTM A928 divides products into five different classes:
Class 1: All welds in the pipe should be double-side welded with filler metal and should be 100% X-ray inspected.
Class 2: All welds in the pipe should be double-side welded with filler metal but do not require X-ray inspection.
Class 3: All welds in the pipe should be single-side welded with filler metal and should be 100% X-ray inspected.
Class 4: All welds in the pipe should be single-side welded with filler metal, but the welds on the inner surface of the pipe may not require filler metal, and should be 100% X-ray inspected.
Class 5: All welds in the pipe should be double-side welded with filler metal and should be inspected by X-ray sampling (at least 300mm per 15m of weld).