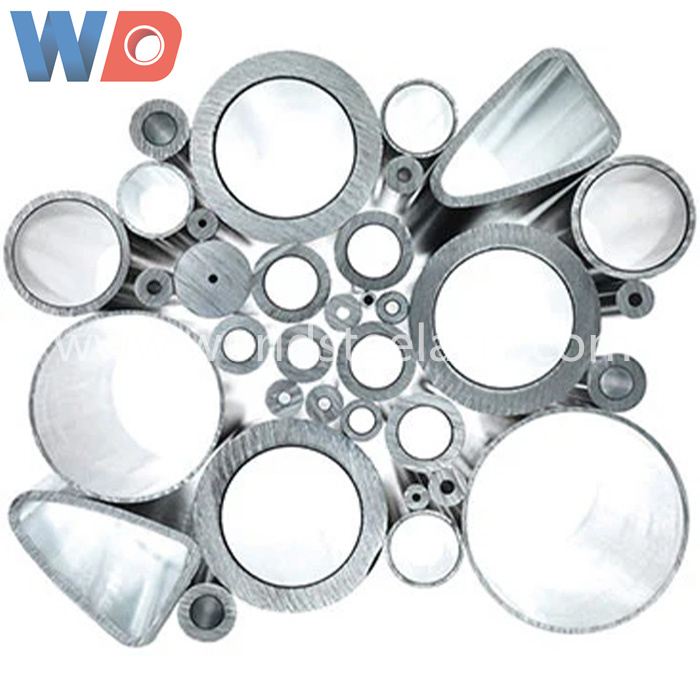
Solution Heat Treated Austenitic Stainless Steel
 AUSTENITIC STAINLESS STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
AUSTENITIC STAINLESS STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
stainless steel \ seamless pipe \ welded pipe \ pipe fittings \ flange \ plate
1. PURPOSE OF AUSTENITIC STAINLESS STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
The matrix structure of austenitic stainless steel is austenite, without martensitic transformation and hardenability during heating and cooling.
The purpose of austenitic heat treatment is to improve corrosion resistance, eliminate the adverse effects of the second phase, eliminate stress, or soften the work hardened material.

2. BASIC THEORY
(1) Precipitation formation temperature
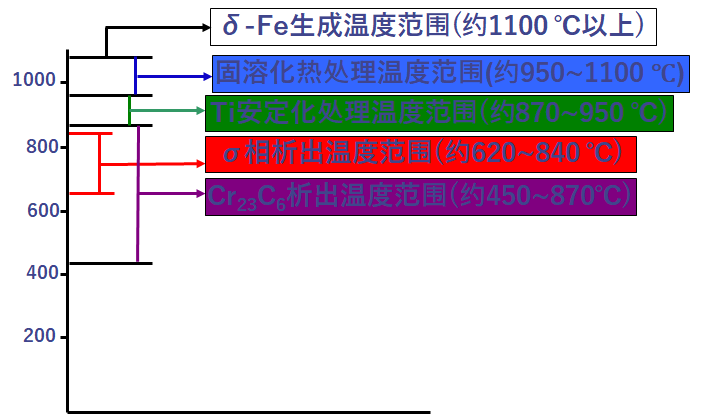
(2) Precipitation and dissolution of alloy carbides
1) Carbon solubility
304 (18Cr-8Ni), solubility of 1200 ℃ carbon is 0.34%, solubility of 1000 ℃ carbon is 0.18%. The solubility of carbon at 600 ℃ is 0.03%.
304 carbon content is not more than 0.08%. Carbon above 1000 ℃ is dissolved in austenite. Due to the small radius of carbon atoms, carbon atoms precipitate along the grain boundary when the temperature decreases.
2) Intergranular chromium deficiency
Carbon solubility: when the temperature decreases, the solubility decreases.
Carbon atom radius: small atom radius, reduced solubility and precipitation along grain boundary.
Stability: the precipitated carbon atoms are unstable and produce stable Cr23C6 or (FeCr) 23c6 with Cr and Fe.
Atomic diffusion rate: the carbon atom has a small radius and a large diffusion rate. Chromium atom has a large radius and a small diffusion rate.
(3) σ mutually
1) Production conditions
620~840 ℃, long-time heating
Add ferrite forming elements, such as Ti, Nd, etc.
The welding rod with high ferrite forming elements is used in the welding seam.
In austenite with Mn and N replacing Ni.
2) Adverse effects
Reduce plasticity, especially impact toughness.
σ The phase is rich in intermetallic compounds, which is easy to cause intergranular corrosion and Cl medium pitting corrosion.
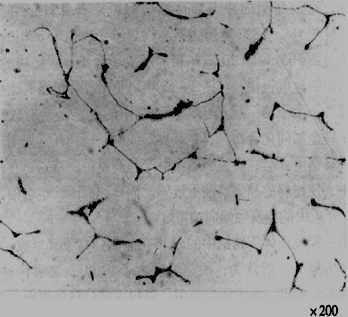
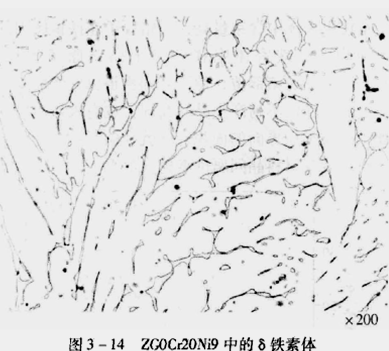
(4) δ- Ferrite
1) Production conditions
Cast chromium nickel austenitic stainless steel has uneven chemical composition as cast, and ferrite forms element segregation zone.
Some austenitic stainless steels are found in the weld structure.
2) Beneficial impact
Including 5-20% δ- Ferrite to reduce intergranular corrosion.
Increase yield strength.
The sensitivity of stress corrosion can be reduced under low stress conditions.
Reduce the possibility of welding hot crack formation during welding
3) Adverse effects
It is easy to form cracks during pressure machining (the deformation capacity of the two structures is different).
3. HEAT TREATMENT PROCESS
(1) Solid solution treatment
1) Solid solution treatment temperature: 950-1150 ℃
2) Holding time: 20-30% longer than that of general alloy steel.
3) Cooling: the carbide formation temperature range (450-850 ℃) needs rapid cooling;
The cooling method has the following principles:
Chromium content is more than 22%, and nickel content is higher;
Carbon content is greater than 0.08%;
Stainless steel with carbon content not greater than 0.08% but effective size greater than 3mm shall be water-cooled.
Stainless steel with carbon content not greater than 0.08% and effective size less than 3mm shall be air-cooled.
Thin parts with effective size less than 0.5mm can be air cooled.
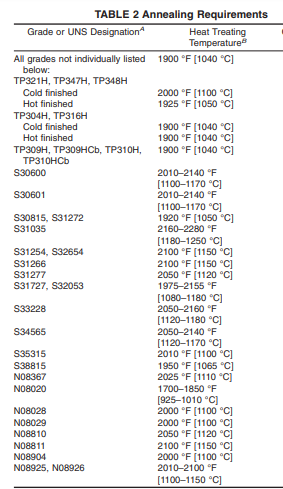
(2) Stabilization treatment
Stabilization treatment is a heat treatment method used for austenitic stainless steel containing nd or Ti.
1) Stabilization treatment temperature: the carbide dissolution temperature higher than chromium (450-870 ℃) is lower than or slightly higher than the dissolution temperature of tic and NBC (750-1120 ℃). 870-950 ℃ is generally recommended.
2) Holding time: 2-4 hours (according to workpiece shape, alloy elements, etc.).
The insulation time of 25mm in thickness or diameter shall be 2 hours, and 1 hour shall be added if it exceeds.
3) Cooling: small cooling rate, such as air cooling or furnace cooling.
(3) Stress relief annealing
1) The stress relief annealing process of austenitic stainless steel shall be selected according to the austenitic stainless steel material, service environment, purpose of stress relief and workpiece shape and size.
2) Purpose of stress relief annealing
Remove residual stress and reduce stress corrosion cracking.
Ensure the stability of the final dimension of the workpiece.
304 304L , 316 316L , 310S , 904L , 309 S , 347 H 321 , Heat treated austenitic stainless steel piping.
from CHONGQING WORLD STEEL CO.,LTD